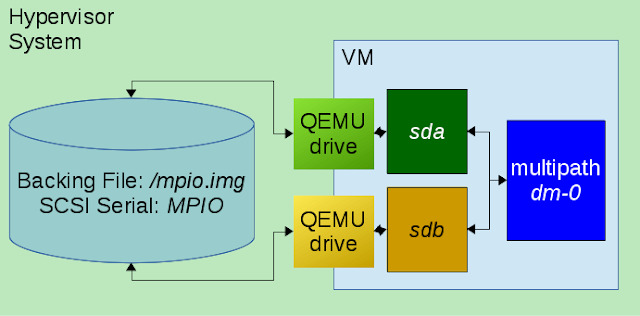
While working on a Ceph OSD multipath issue, I came across a
helpful post from Dan Horák on how to simulate a multipath device under QEMU.
qemu-kvm ... -device virtio-scsi-pci,id=scsi \
-drive if=none,id=hda,file=<path>,cache=none,format=raw,serial=MPIO \
-device scsi-hd,drive=hda \
-drive if=none,id=hdb,file=<path>,cache=none,format=raw,serial=MPIO \
-device scsi-hd,drive=hdb"
- <path> should be replaced with a file or device path (the same for each)
- serial= specifies the SCSI logical unit serial number
This attaches two virtual SCSI devices to the VM, both of which are backed by the same file and share the same SCSI logical unit identifier.
Once booted, the SCSI devices for each corresponding path appear as
sda and
sdb, which are then detected as multipath enabled and subsequently mapped as
dm-0:
Starting Device-Mapper Multipath Device Controller...
[ OK ] Started Device-Mapper Multipath Device Controller.
...
[ 1.329668] device-mapper: multipath service-time: version 0.3.0 loaded
...
rapido1:/# multipath -ll
0QEMU_QEMU_HARDDISK_MPIO dm-0 QEMU,QEMU HARDDISK
size=2.0G features='1 retain_attached_hw_handler' hwhandler='0' wp=rw
|-+- policy='service-time 0' prio=1 status=active
| `- 0:0:0:0 sda 8:0 active ready running
`-+- policy='service-time 0' prio=1 status=enabled
`- 0:0:1:0 sdb 8:16 active ready running
QEMU additionally allows for virtual device hot(un)plug at runtime, which can be done from the QEMU monitor CLI (accessed via
ctrl-a c) using the
drive_del command. This can be used to trigger a multipath failover event:
rapido1:/# mkfs.xfs /dev/dm-0
meta-data=/dev/dm-0 isize=256 agcount=4, agsize=131072 blks
= sectsz=512 attr=2, projid32bit=1
= crc=0 finobt=0, sparse=0
data = bsize=4096 blocks=524288, imaxpct=25
= sunit=0 swidth=0 blks
naming =version 2 bsize=4096 ascii-ci=0 ftype=1
log =internal log bsize=4096 blocks=2560, version=2
= sectsz=512 sunit=0 blks, lazy-count=1
realtime =none extsz=4096 blocks=0, rtextents=0
rapido1:/# mount /dev/dm-0 /mnt/
[ 96.846919] XFS (dm-0): Mounting V4 Filesystem
[ 96.851383] XFS (dm-0): Ending clean mount
rapido1:/# QEMU 2.6.2 monitor - type 'help' for more information
(qemu) drive_del hda
(qemu)
rapido1:/# echo io-to-trigger-path-failure > /mnt/failover-trigger
[ 190.926579] sd 0:0:0:0: [sda] tag#0 UNKNOWN(0x2003) Result: hostbyte=0x00 driverbyte=0x08
[ 190.926588] sd 0:0:0:0: [sda] tag#0 Sense Key : 0x2 [current]
[ 190.926589] sd 0:0:0:0: [sda] tag#0 ASC=0x3a ASCQ=0x0
[ 190.926590] sd 0:0:0:0: [sda] tag#0 CDB: opcode=0x28 28 00 00 00 00 02 00 00 01 00
[ 190.926591] blk_update_request: I/O error, dev sda, sector 2
[ 190.926597] device-mapper: multipath: Failing path 8:0.
rapido1:/# multipath -ll
0QEMU_QEMU_HARDDISK_MPIO dm-0 QEMU,QEMU HARDDISK
size=2.0G features='1 retain_attached_hw_handler' hwhandler='0' wp=rw
|-+- policy='service-time 0' prio=0 status=enabled
| `- 0:0:0:0 sda 8:0 failed faulty running
`-+- policy='service-time 0' prio=1 status=active
`- 0:0:1:0 sdb 8:16 active ready running
The above procedure demonstrates cable-pull simulation while the broken path is used by the mounted
dm-0 device. The subsequent I/O failure triggers multipath failover to the remaining good path.
I've added this functionality to
Rapido (
pull-request) so that multipath failover can be performed in a couple of minutes directly from kernel source. I encourage you to give it a try for yourself!